Configuration¶
In order to configure Passivbot, you will need to provide a json file when starting the bot.
These config files are typically stored in the config/live.
Info
The configuration of telegram is not covered in this chapter. Please refer to Telegram for configuring Telegram.
Configuration options¶
In the configuration file provided to run live, the parameters mentioned in the table can be set. The configuration is split in 4 categories for clarity (user, initial entry, reentry, taking profit, stoploss). A more detailed explanation on each configuration option is given later on in this chapter.
It's important to realize that most of the configuration is split across a configuration for short positions and long positions.
Configuration parameters that this applies to, are prepended with short§long: in the configuration table below.
Info
The config file can be quite overwhelming when looking at it for the first time. You can have a look at the configuration files provided in the repository by default to get a feel for config files.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
config_name |
A user-defined identification of the file Category: User Datatype: String |
logging_level |
Indication if logging is to be written to file 0: Don't write to logfile 1: Write to logfile Category: User Datatype: Integer |
short§long:enabled |
Enables/disables the applicable position side Category: User Datatype: Boolean |
allow_sharing_wallet |
Indicates if the bot is allowed to start when a position already exists on another symbol Category: User Datatype: Boolean |
last_price_diff_limit |
Determines until what price the orders are calculated up front Category: User Datatype: Float |
n_spans |
Number of spans used to determine initial entry Category: Initial entry Datatype: Integer |
max_spans |
Maximum number of ticks used in MA spans Category: Initial entry Datatype: Float |
min_spans |
Minimum number of ticks used in MA spans Category: Initial entry Datatype: Float |
short§long:pbr_limit |
Position cost to balance ratio limit Category: Initial entry Datatype: Float |
short§long:iprc_MAr_coeffs |
Initial price Mean Average coefficients Category: Initial entry Datatype: [[Float,Float]..] |
short§long:iprc_const |
Initial price constant Category: Initial entry Datatype: Float |
short§long:iqty_const |
Initial quantity percentage of balance Category: Initial entry Datatype: Float |
short§long:iqty_MAr_coeffs |
Initial quantity Mean Average coefficients Category: Initial entry Datatype: [[Float, Float]..] |
short§long:rprc_const |
Reentry price constant Category: Reentry Datatype: Float |
short§long:rqty_const |
Reentry quantity constant Category: Reentry Datatype: Float |
short§long:rprc_PBr_coeffs |
Reentry position cost to balance ratio coefficients Category: Reentry Datatype: [[Float, Float]..] |
short§long:rqty_MAr_coeffs |
Reentry quantity Mean Average coefficients Category: Reentry Datatype: [[Float, Float]..] |
short§long:rprc_MAr_coeffs |
Reentry price Mean Average coefficients Category: Reentry Datatype: [[Float, Float]..] |
short§long:markup_const |
Profit markup constant Category: Taking profit Datatype: Datatype: Float |
short§long:markup_MAr_coeffs |
Markup Mean Average coefficients Category: Taking profit Datatype: [[Float, Float]..] |
short§long:pbr_stop_loss |
Position cost to balance ratio stoploss Category: Stoploss Datatype: Float |
profit_trans_pct |
Percentage indicating how much profit should be transferred to Spot wallet on each order filled Category: Closing Datatype: Float |
cross_wallet_pct |
Percentage of the total wallet that is used in calculating orders Category: User Datatype: Float |
Initial trade entry¶
Once the bot has started, it will start to create limit orders to enter a position. Depending on whether you have long and/or short enabled it will create limit orders for either side. The bot relies uses Exponential Moving Averages to calculate the entry points and stoplosses. When you look at a chart with the initial entry orders, the chart will typically look like this:
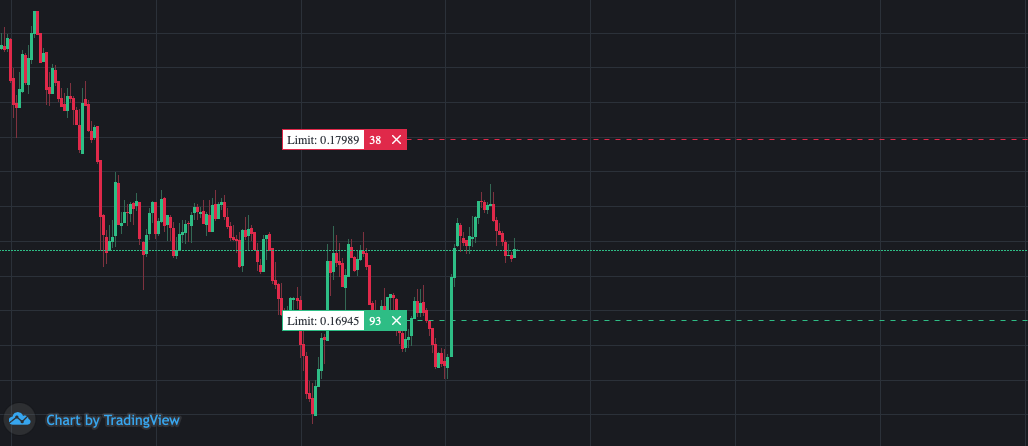
What you see on the chart are two limit orders: one above the current price for entering a short position, and the other below the current price for entering a long position.
Info
While looking at the chart on your exchange can be helpful, it's often not very practical. If you've got Telegram
set up, you can also get an overview of the limit orders by using the /open_orders command.
The price of the first limit order is calculated as follows:
long = lower_EMA_band * iprc_const
short = upper_EMA_band * iprc_const
The EMA upper and lower band (depending on short or long) are calculated by taking the minimum and maximum value of the different EMAs. The bot calculates EMA based on raw trades (also referred to as ticks) using the following formula:
ema = prev_ema * (1 - alpha) + tick_price * alpha
alpha = 2 / (span + 1)
The fastest EMA is defined by the configuration parameters min_spans, while the slowest EMA is defined by the configuration parameter max_spans.
The configuration parameters n_spans defines the number of spans used in the calculation.
An example of the entry price for a short limit order for initial entry:
Given that the iprc_const is 1.005
And that the EMAs are [33.4, 32.1, 32.9]
Then the initial entry price is calculated as 33.4 * 1.005 = 33.567
The size of the inital entry order is calculated as follows:
balance_in_terms_of_contracts * iqty_const
An example of the entry size for a short limit order for initial entry:
Given that the iqty_const is 0.03
And that the balance is $200
Then the initial entry will is calculated as $200 * 0.03 = $6
The configuration parameters MAr_coeffs can modify how the ratio between the EMA spans are calculated.
This can be disabled by setting these configuration parameters to 0.0.
Reentry¶
Once the bot is in a position, it will calculate a potential next reentry on the same position side. This allows the bot to keep the closing price close to the reentry price, allowing it to (if all goes well) close the position in profit without requiring the price to retract to the initial entry price for making profit. In order to so, the reentries will be bigger in quantity on each reentry in order to compensate for the existing position. As long as there is sufficient balance, the bot will keep creating reentry orders based on the previous reentry order until the allowed balance is spent. A chart with a position on both sides will tyically look like this:
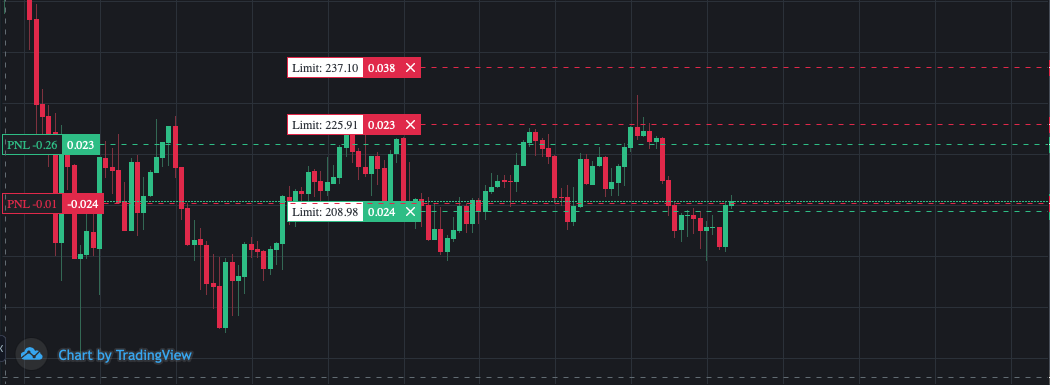
On the chart you can see there are currently two positions open (the two PNL lines are an indication of this, which indicate the entry price). Right beyond those PNL lines are the limit orders for taking profit. In the chart you see above, there is also another limit order at the top, which is the first reentry order for the short position.
Info
Depending on your configuration, you may not (yet) see all possible reentries. The bot will only create the orders that are
within 15% of the current price. This way, the bot can avoid running into rate limit issues. If you want to see more reentry
orders that are further away, you can set the configuration parameter last_price_diff_limit to a value between 0 and 1 (1
being 100%)
The next reentry price is calculated using the following formula:
long = min(initial long entry price, long position price * long§rprc_const)
short = max(initial short entry price, short position price * short§rprc_const)
Apart from using the above formula to calculate the next reentry price, the long§rprc_PBR_coeffs parameters are used
to modify the grid space in proportion to the position size.
The ratio of position cost to balance times PBr_coeffs is added to rprc_const. An example of how this influences the reentry price:
Given that the current position size is 0.23
And that the position price is 250.0
And that the balance is $80.0
Then the position cost is 0.23 * 250.0 = 57.5
And position cost to balance ratio is 57.5 / 80 = 0.71875
In order to determine the reentry price modificatier, the following formula is used:
Reentry price modified = position cost to balance ratio ** 2 * PBr_coeffs[0] + position cost to balance ratio * PBr_coeffs[1]
Let's look at an example on calculating the next reentry for a long position to illustrate this:
Given that the reentry price constant is 0.98
And the PBr_coeffs is [-0.05, 0.01]
Then the reentry price is rprc_const + 0.71875**2 * -0.05 + 0.71875 * 0.01 == 0.98 + -0.018642578125000003 == 0.961357421875
And the next reentry will be ~3.86% instead of 2.0% lower than long position entry price.
The next reentry quantity is calculated using the following formula:
order_size = initial entry quantity + position size * short§rqty_const
Info
When reentry limit orders are calculated, any reentry order that makes the position cost higher than pbr_limit + pbr_stoploss is not created.
Closing trades¶
Once a position is opened, it can either be closed when it is in profit, or get into a stoploss position. Both situations are described in the following sections.
Taking profit¶
Once the position reaches a predefined price, it will be closed, resulting in profit to be taken. The closing order for this is calculated up front. The price at which the entire position will be closed is calculated using the following formula:
closing_price = position_price * markup_const
As you can see in the formula, increasing the markup_const will increase the profit. Be aware that the price will also
need to move further to reach that price though!
Stoploss¶
Passivbot may under some circumstances partially close a position at a loss.
This happens if config's pbr_stop_loss > 0.0 and a position's pbr is greater than config's pbr_limit.
A position's pbr may grow to maximum pbr_limit + pbr_stoploss.
Stop loss amount is max(0, pbr - pbr_limit), that is, position is reduced at a potential loss such that pbr <= pbr_limit.
Stop loss orders are not necessarily filled immediately. Long stop loss price is never lower than upper ema band and short stop loss price is never higher than lower ema band.
Logging¶
When running, Passivbot writes information to the console by default. It is possible to have the bot write this information to a log file for easier access and to allow looking up information historically. This information includes orders being created, cancelled, positions and open orders.
If the configuration parameter logging_level is set to 0, the aforementioned information will not be written to a logfile.
If the parameter is set to 1, the information will be written to a logfile.
If writing the logs to a file is enabled, the information is stored in a file at logs/{exchange}/{config_name}.log.
The config_name is the value that is specified in the config_name parameter in the configuration file.
Warning
Be aware that Windows can have a limitation on the maximum path length of a file. If you run into a problem with this,
you can try moving Passivbot to a different location that results in a shorter pathname, or a shorter value in the config_name parameter.
Automatic profit transfer¶
Passivbot provides functionality to automatically transfer a specified percentage of profit on closed trades to the spot wallet.
The transfer is performed in USDT, and the percentage transferred is defined by the profit_trans_pct configuration parameter.
Besides automatic profit transfer, you can also manually transfer funds between your spot and futures wallet using Telegram. You can read more on this functionality in the Telegram section.
Info
In order to use this functionality, make sure you enable Universal Transfer on your API key.
This functionality is currently only supported on Binance
Limit wallet balance used¶
To make the bot even safer than a good config already makes it, you may choose to limit the amount of total wallet balance to be used by the bot. Since the bot opens positions in cross mode, this will give your bot an extra buffer in case of unforeseen extreme volatility in the market.
To limit the bot to only use a certain percentage of the entire wallet balance, you can set the parameter cross_wallet_pct. If not set, the
parameters defaults to 1.0, meaning the bot will be allowed to utilize the entire wallet for opening positions. For example, when you set the
value to 0.1, the bot will only utilize 10% of the total wallet balance.
Running multiple instances¶
It is possible, however not recommended to launch multiple configs of the bot on one wallet. This setup is considered advanced and it's up to the user to configure it properly. Here are a few things to take into consideration:
- Utilize
cross_wallet_pctto limit amount of the wallet used per config. - Use only configs tested on a long timeframe with wide range of market conditions that have high bankruptcy distance.
To start with you have to create an extra user in the api_keys.json file for each configuration you want a bot instsance to run, but the api keys for the exchange can be copied to multiple passivbot users.
In order to use telegram with multiple passivbotbot instances, you'll need to have a separate telegram bot and accompanying token per bot instance. A single telegram bot can not be used with multiple passivbot instances and will cause errors.
{
"binance_01" : {
"exchange": "binance",
"key": "key",
"secret": "secret",
"telegram": {
"enabled": true,
"notify_entry_fill": true,
"notify_close_fill": true,
"token": "bot_token1",
"chat_id": "chat_id"
}
},
"binance_02" : {
"exchange": "binance",
"key": "key",
"secret": "secret",
"telegram": {
"enabled": true,
"notify_entry_fill": true,
"notify_close_fill": true,
"token": "bot_token2",
"chat_id": "chat_id"
}
},
}